Production Of Transgenic Animals Notes
Milk as the Medium of Protein Production.
Production of transgenic animals notes. To yield industrial as well as consumer product To research human diseases To produce pharmaceutical products and tissue for implantation. The medical and biotechnological uses of animal cloning are almost innumerable as many diseases have been eradicated thanks to the production of these transgenic animals. Let us discuss a few of them here.
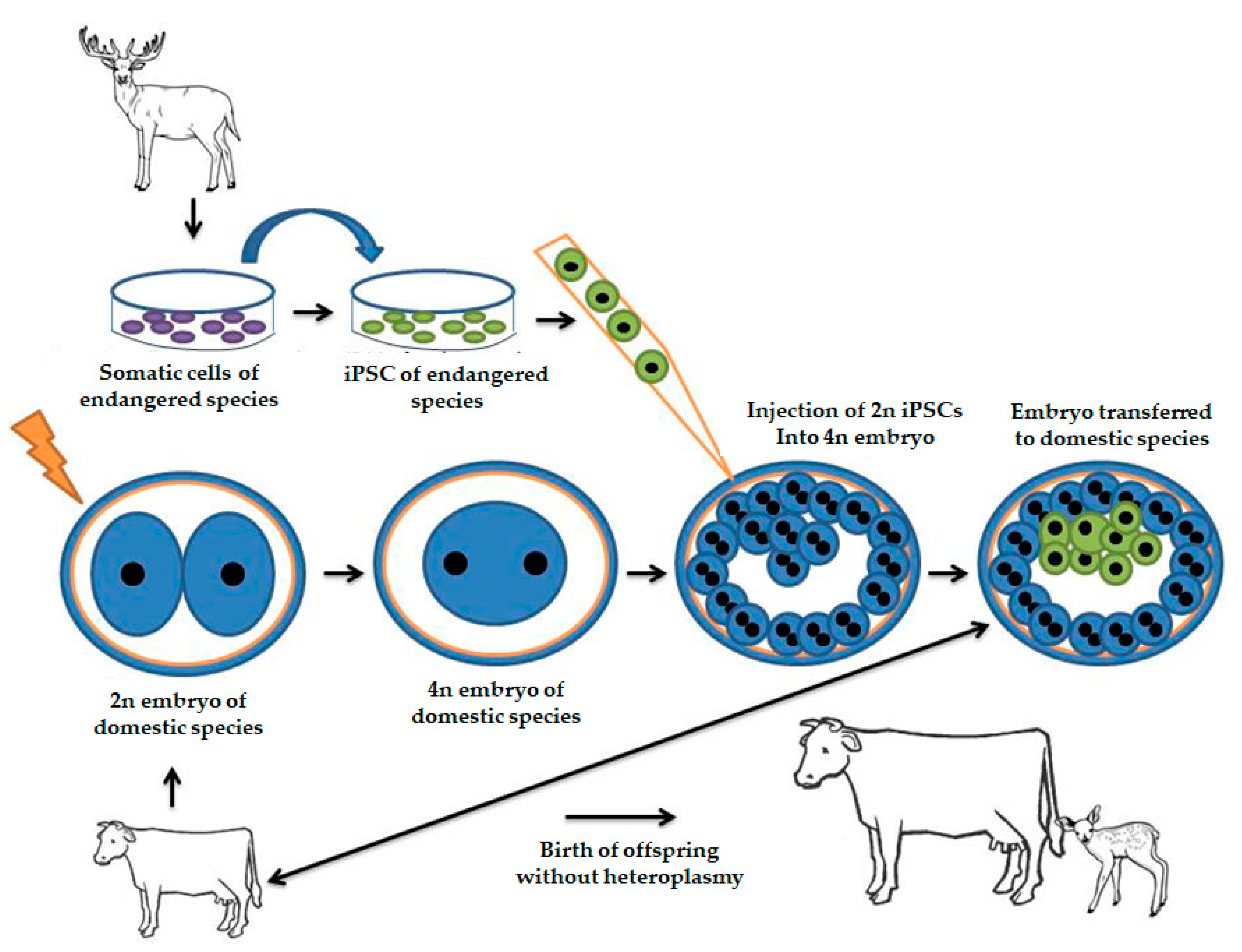
ES cells are obtained from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst. Then they are inserted into a blastocyst and implanted into a hosts uterus to grow normally. Milk is the secretion of mammary glands that can be collected frequently without causing any harm to the animal.
The transgenic expression is not only used to breed animals which have specific traits but also to breed animals that are lacking specific genes This technique is called as knockout or gene. Theses mechanism is absent in cell culture. Benefits of Transgenic Animals The benefits of these animals to human welfare can be grouped into areas.
Transgenic animals are being used to study gene mechanism and function to adapt pig organs to be transferred to humans to prepare recombinant pharmaceutical proteins in milk and egg white and to improve breeding and food production. After injecting the DNA the embryo is implanted into the uterus of receptive females. Studying gene function.
PowerPoint PPT presentation. Microinjection blastocyst injection and using a retrovirus Nuclear transfers Artificial chromosomes for gene transfer PRODUCTION OF TRANSGENIC ANIMALS THE METHODOLOGY. Transgenic mice are developed by injecting DNA into the oocytes or 1-2 celled embryos taken from female mice.
The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA methodology. Transgenic animals are created-To study how genes are regulated and how they affect the normal functions of the body and its development. Transgenic animals produced with the purpose of producing better and good quality breed increased in milk yield as well as to produce organs to meet the demand for organ transplantation.