Food Chain Definition Ecology

Food chain definition ecology Thinking Food Chain Definition Ecology to Eat.
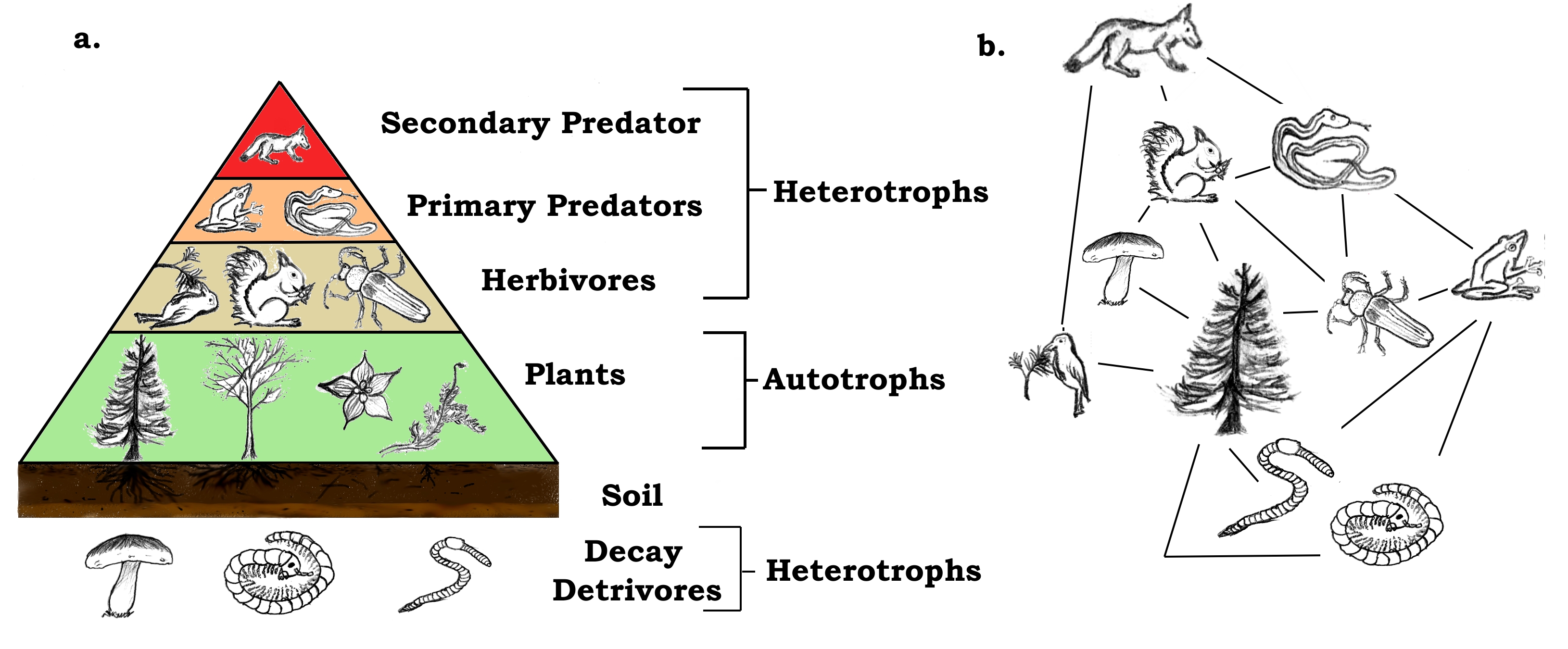
Food chain definition ecology. The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy is transferred from one organism to the other. The food chain consists of four major parts. That is they can form one of the links in a food chain.
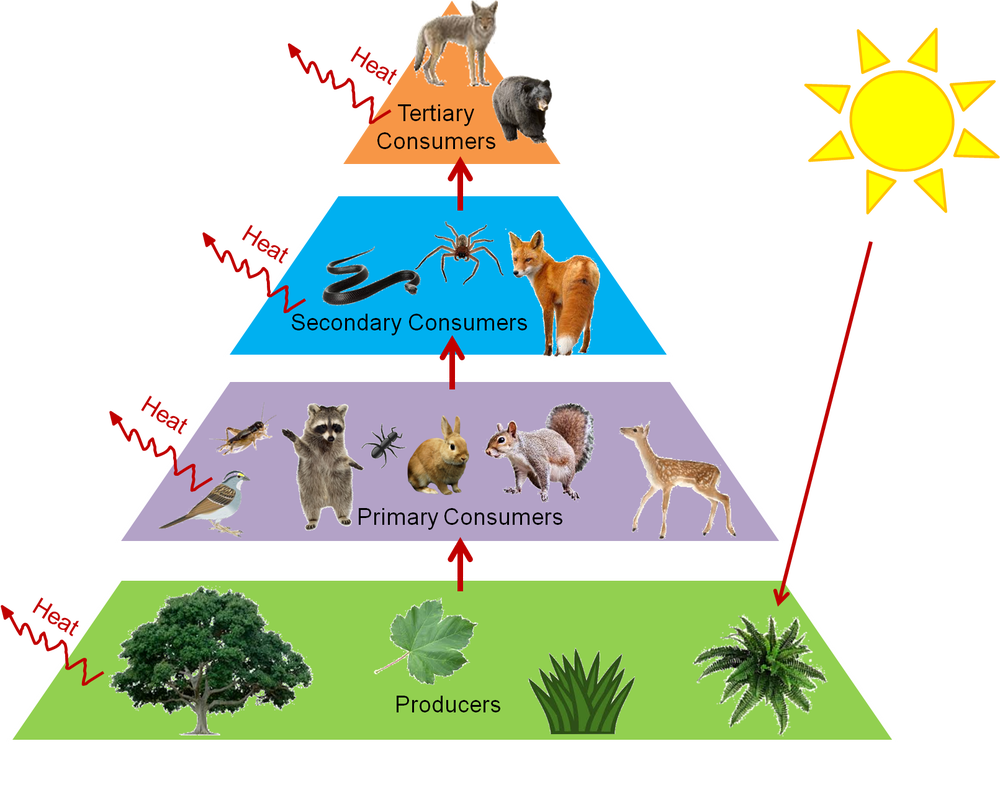
The sun is the initial source of energy which provides energy for everything on the planet. The term food chain describes the order in which organisms or living things depend on each other for food. The idea to apply the food chains to ecology and to analyze its consequences was first proposed by Charles Elton Krebs 2009.
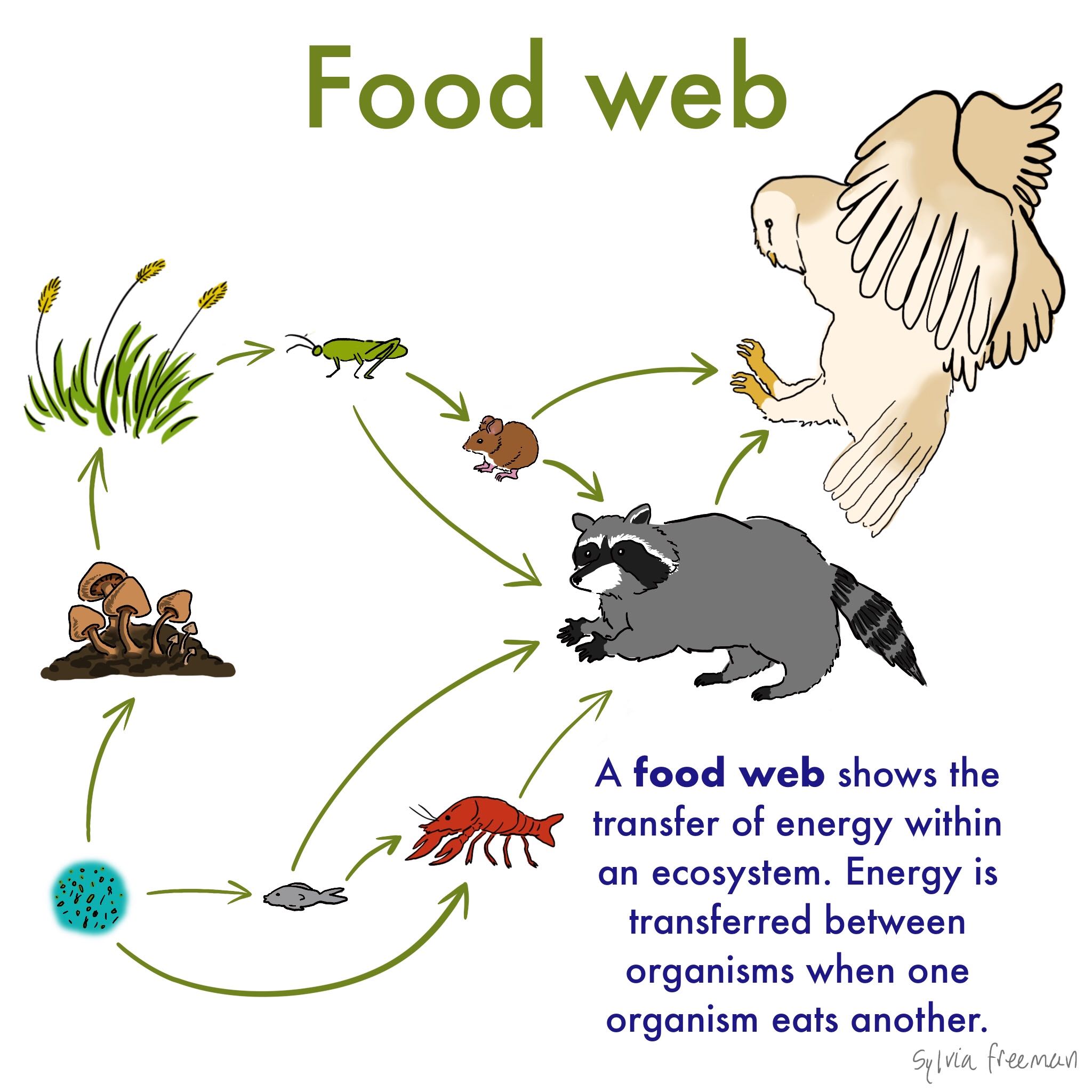
Each food chain is a possible pathway that energy and nutrient s can follow through the ecosystem. From the examples given above we can understand that how the food material forms consumers of different levels of the food chain based on producers. The food chain describes who eats whom in the wild.
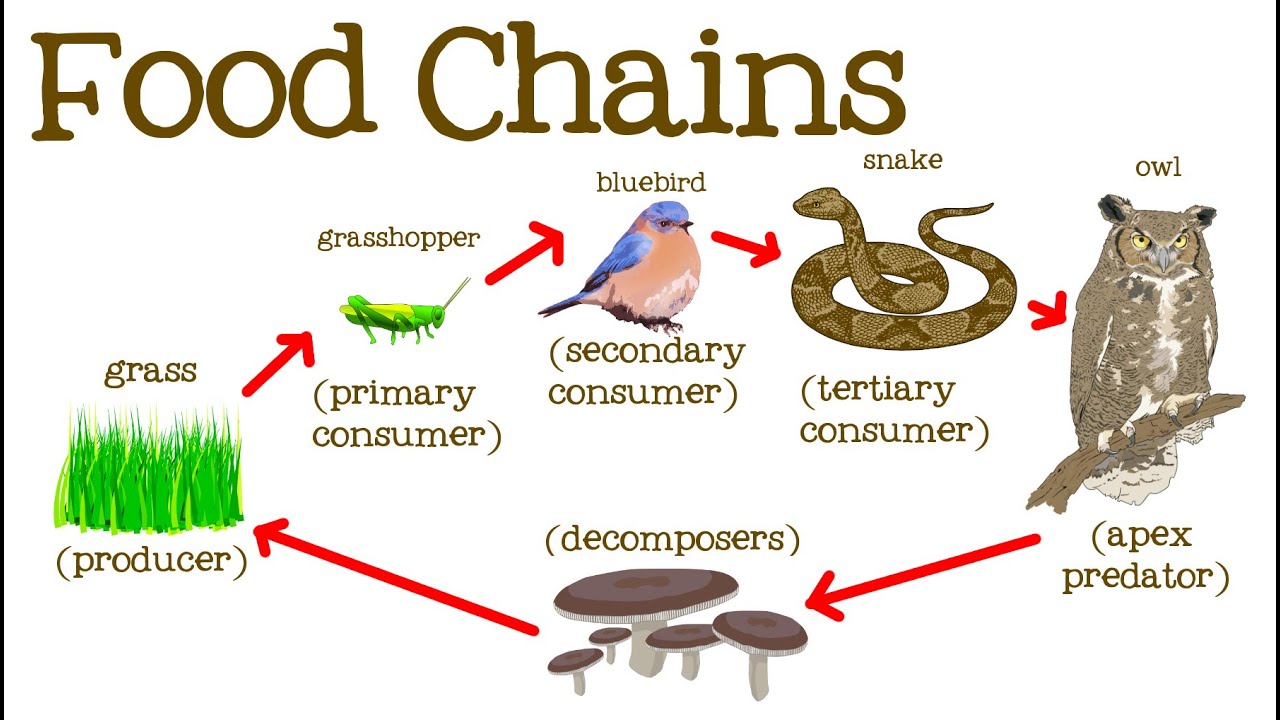
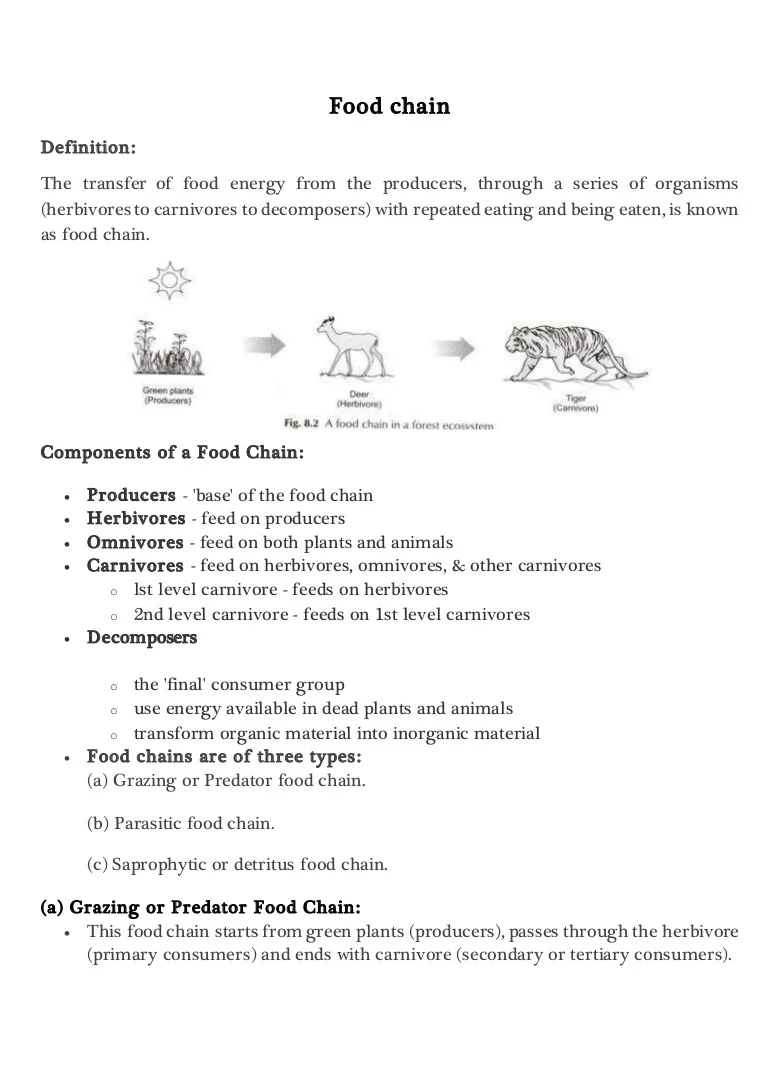
A food chain in a grassland ecosystem may consist of grasses and other plants grasshoppers frogs snakes and hawks figure 83. Food chain - ecology a community of organisms where each member is eaten in turn by another member bionomics environmental science ecology - the branch of biology concerned with the relations between organisms and their environment. Food Chains - BrainPOP.
A food chain begins with a producer usually a green plant or alga that creates its own food through photosynthesis. It shows the flow of energy and materials from one organism to the next beginning with a. Plants are eaten by insects insects are eaten by frogs the frogs are eaten by fish and fishes are eaten by humans.
The sequence of the transfer of food energy from one organism to another in an ecological community. The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy are transferred from one organism to another. This cyclic transfer of food and the relation of food and its consumer are known as the food chain.