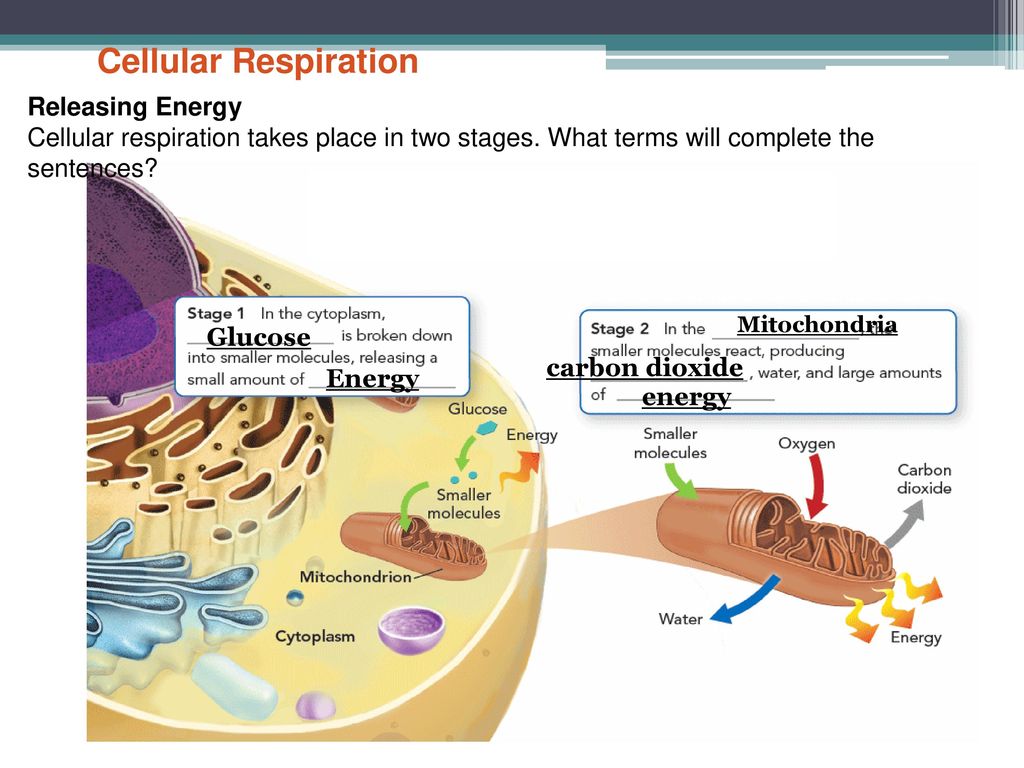
Cellular Respiration Takes Place In Two Stages

Respiration takes place in the two stages are External respiration The exchange of gases between the environment and the body is called external respiration or gaseous exchange.
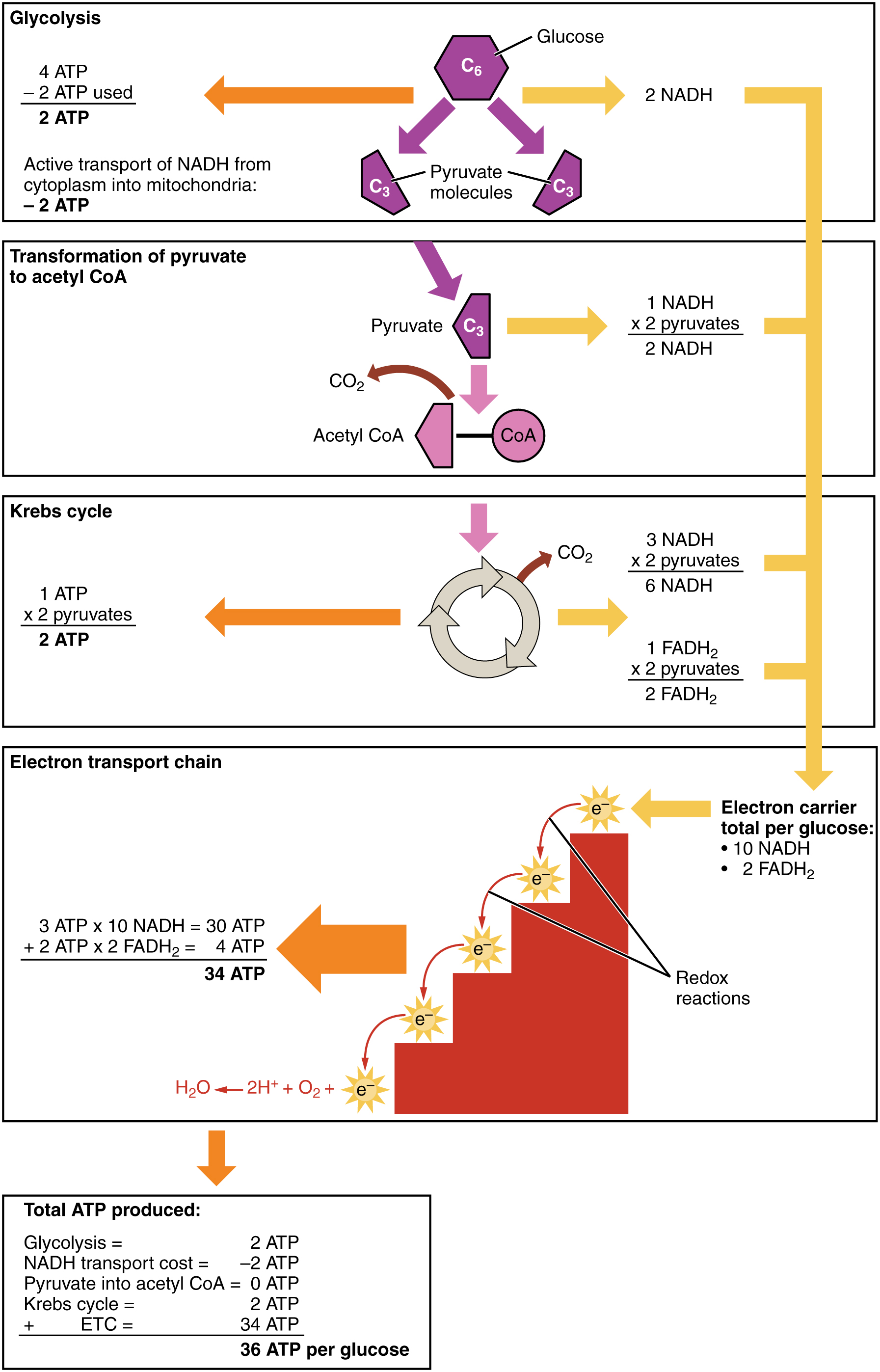
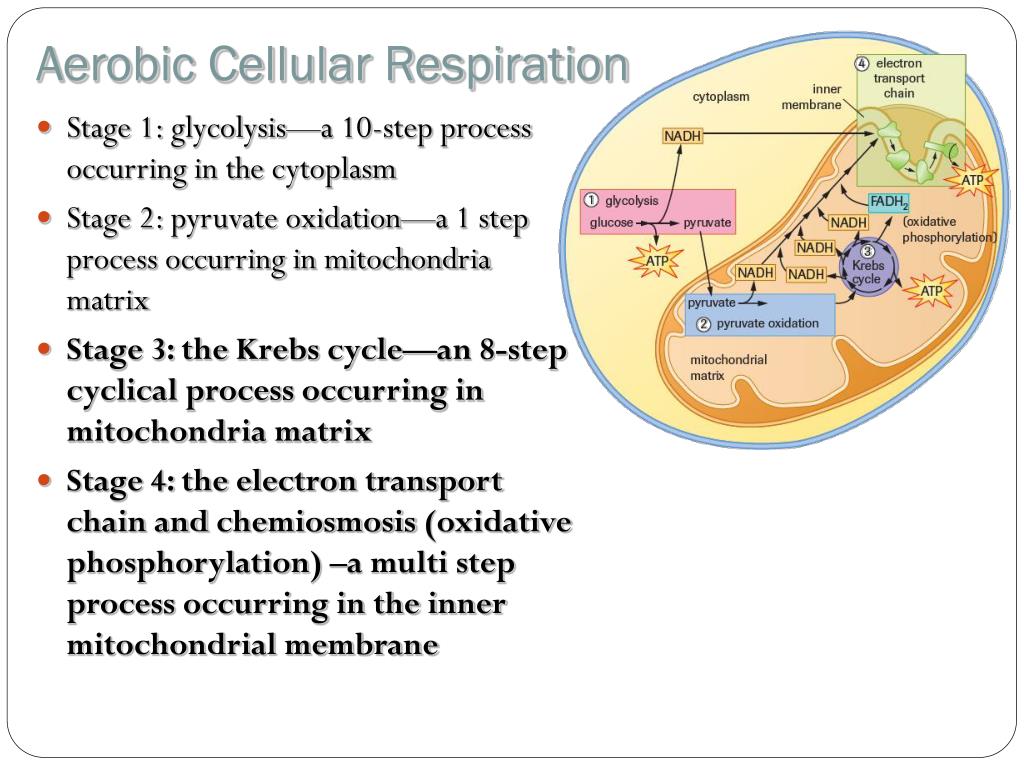
Cellular respiration takes place in two stages. Glycolysis the Krebs cycle and electron transport. The stages in aerobic respiration are. Cellular respiration takes place in 2 stages What are the two stages of respiration.
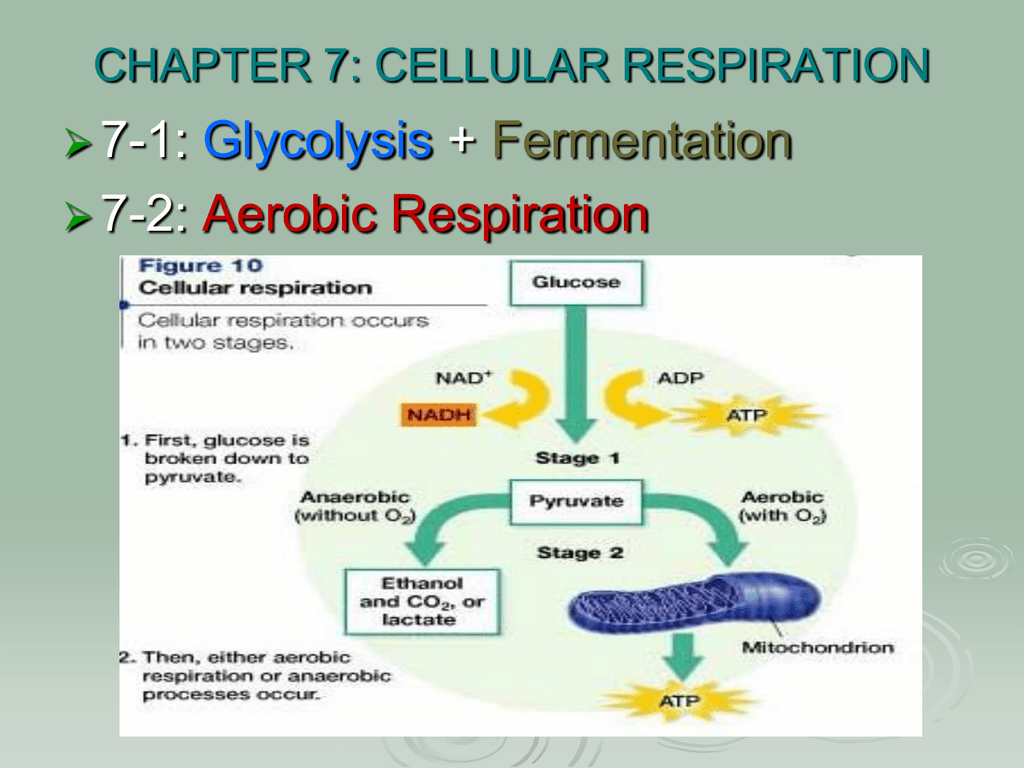
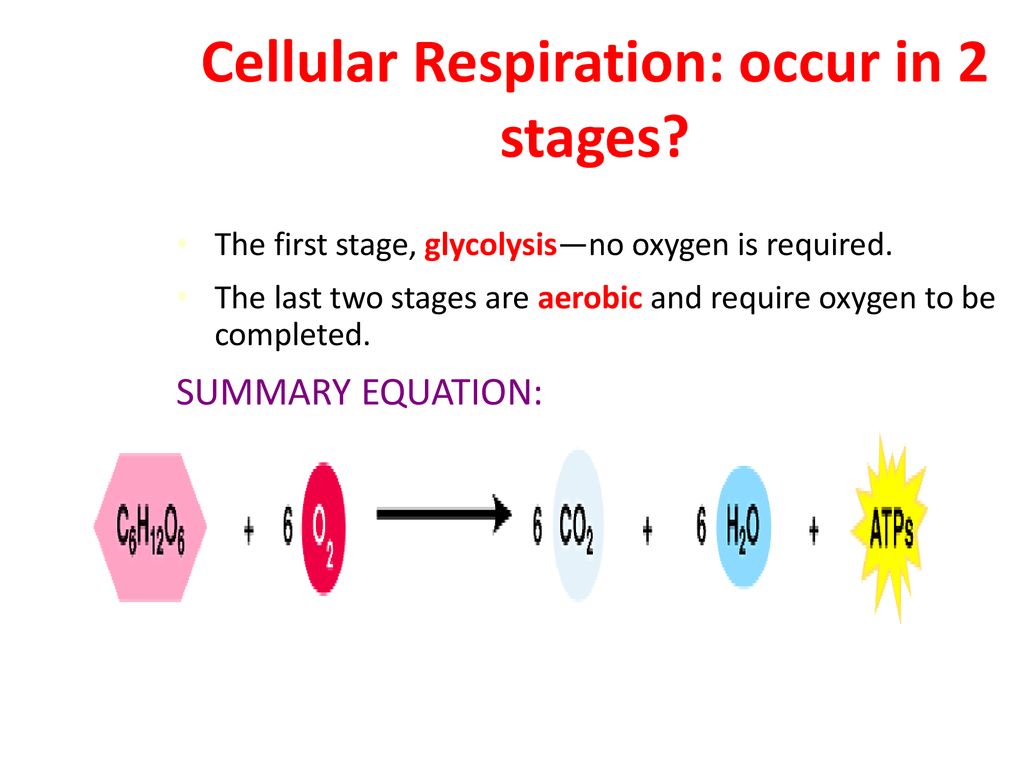
The other two stages are aerobic processes. It breaks down glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 into pyruvate CH 3 COCOO H. Anaerobic Respiration The first step in cellular respiration in all living cells is glycolysis which can take place without the presence of molecular oxygenIf oxygen is present in the cell then the cell can subsequently take advantage of aerobic respiration via the TCA cycle to produce much more usable energy in the form of ATP than any anaerobic pathway.
The first step of cellular respiration glycolysis occurs in the cytosol. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions that take place in all living cells to release energy by converting biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate- ATP. The net effect is that it splits 6 carbon rings of glucose into two 3-carbon molecules called pyruvic acids.
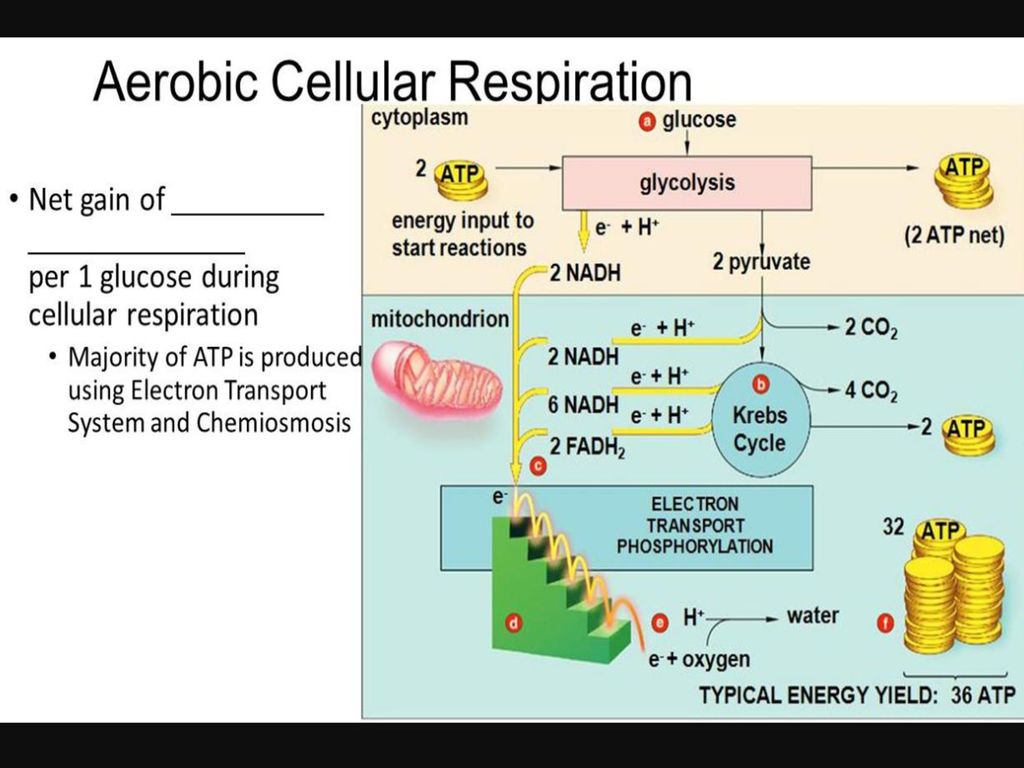
Simultaneously these 3 phases of cellular respiration produce the following number of ATP. There are three main stages of cellular respiration. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm without oxygen.
Likewise biological machines also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to workPerhaps the second most important molecule DNA is the first is adenosine triphosphate also known as ATPBasically ATP serves as the main energy currency of the cell. Glycolysis Krebs cycle and electron transport chain anaerobic respiration. This pathway is anaerobic and takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell.
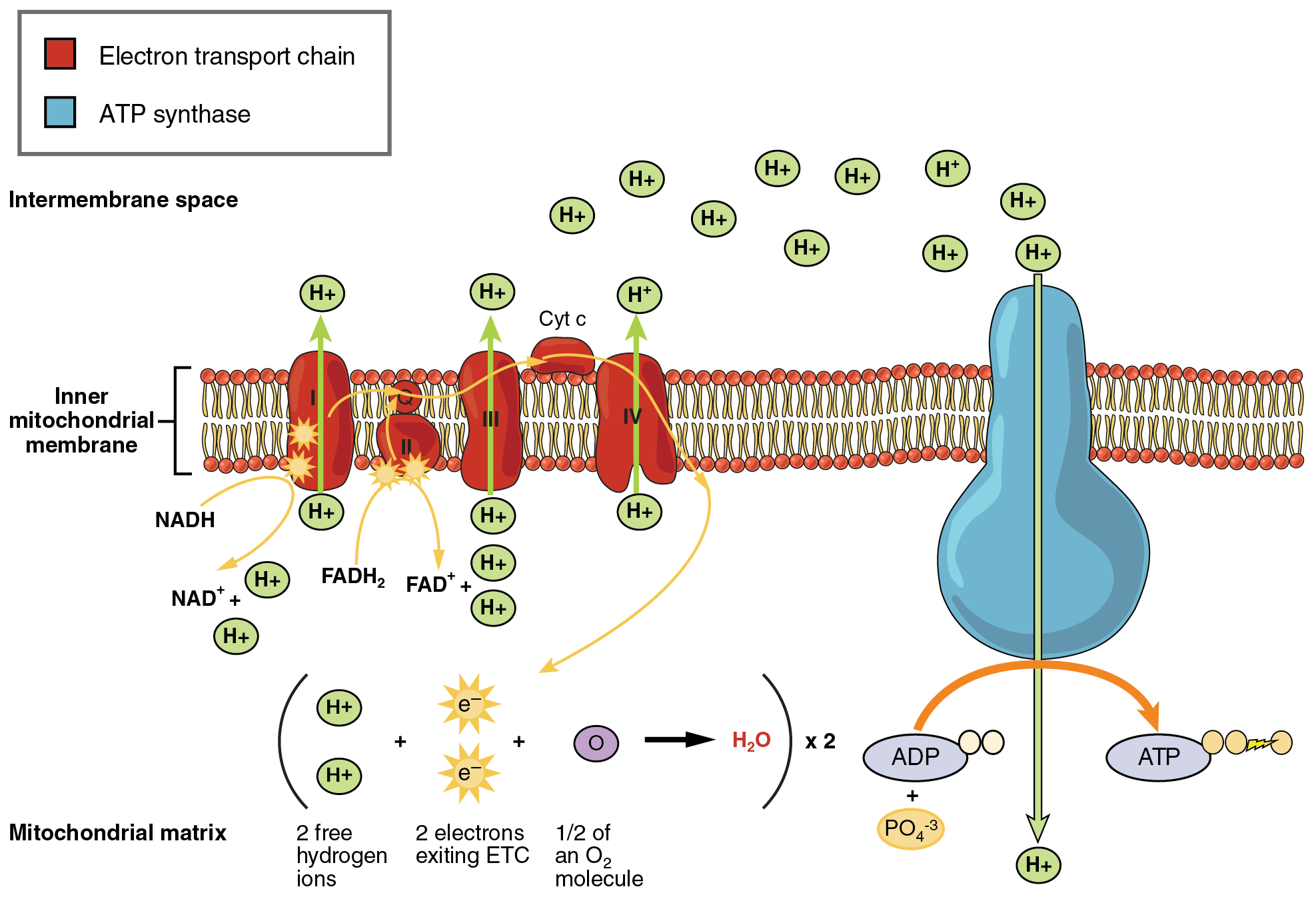
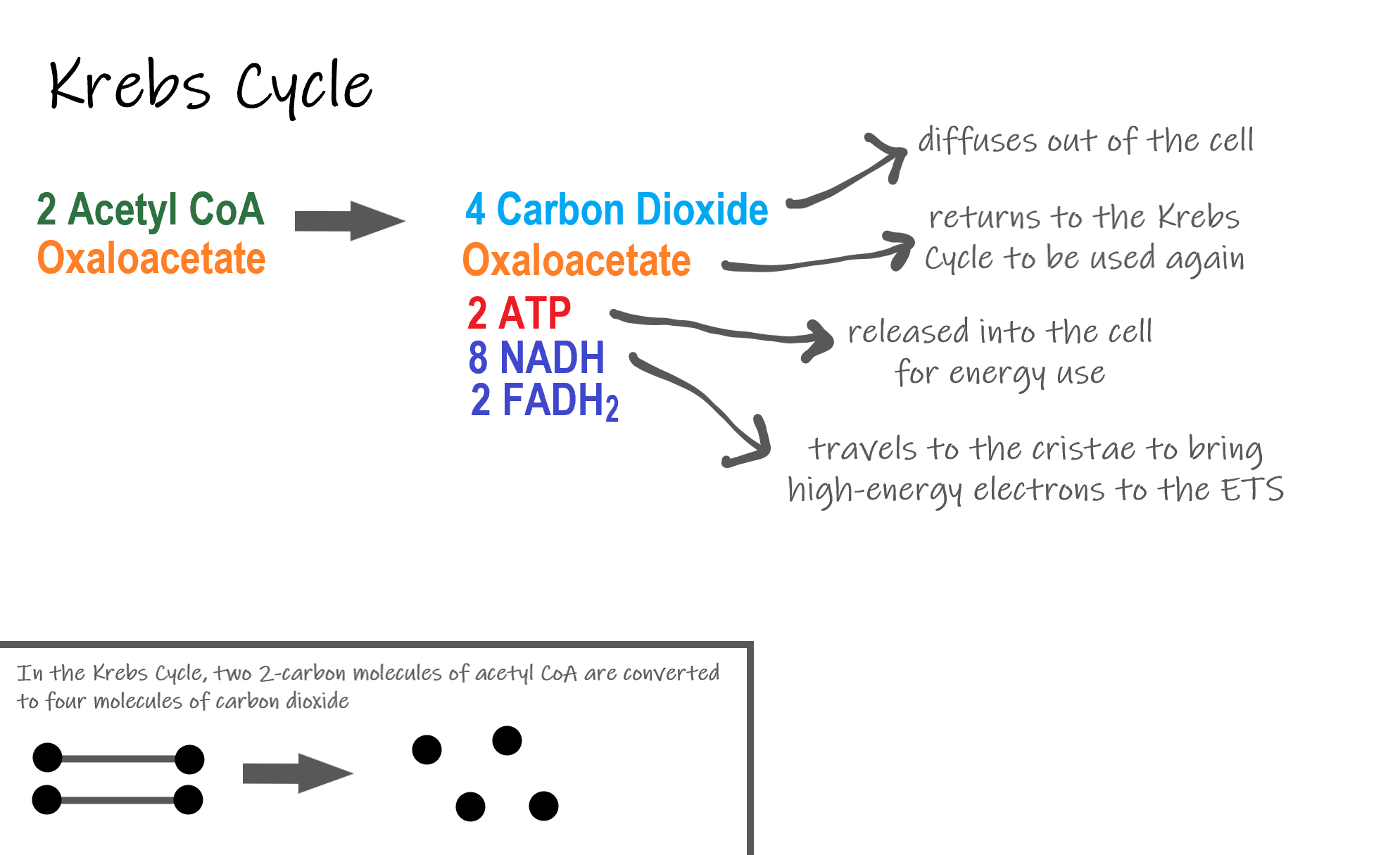
Glycolysis generates 2 ATP. Curbs cycle or citric acid cycle. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.


/respiration-58b9a1d93df78c353c0e3e0f.jpg)






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration_3-58b9a5415f9b58af5c839e04.jpg)
