Cellular Respiration Equation Definition

It is a type of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen to produce energy.
Cellular respiration equation definition. This series of biochemical reactions is also called a metabolic pathway Two types of cellular respiration exist. It occurs within the cells of all living organisms including both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Cellular Respiration Definition.
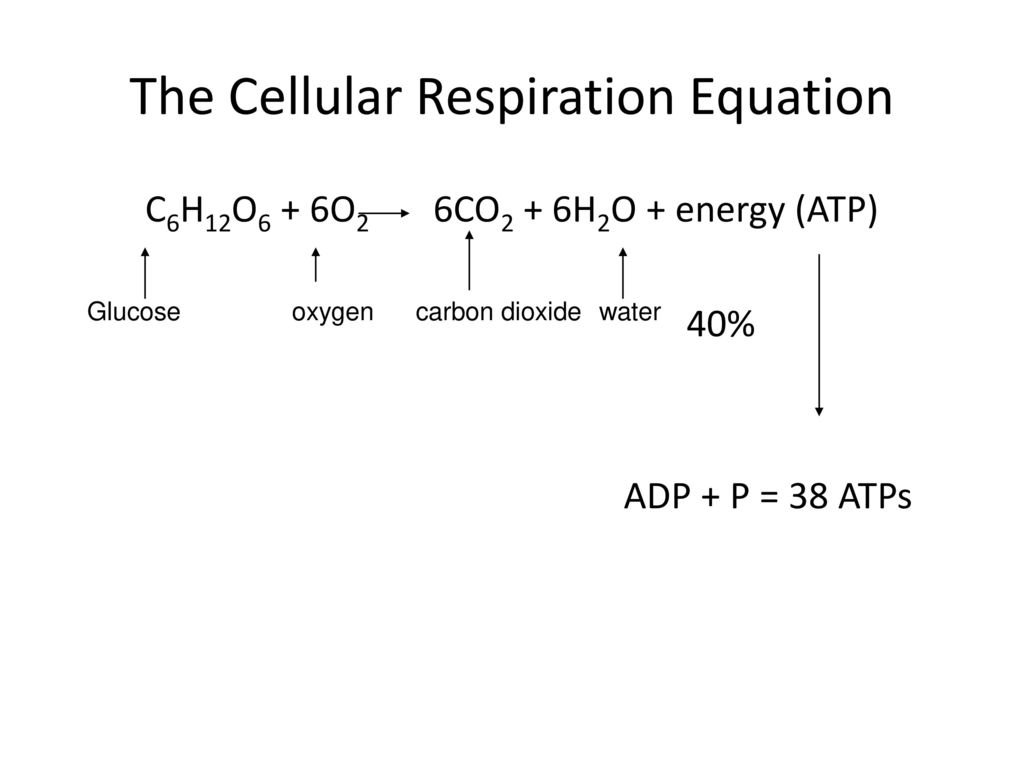
Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate ATP and then release waste products. In this process water and carbon dioxide are produced as end products.
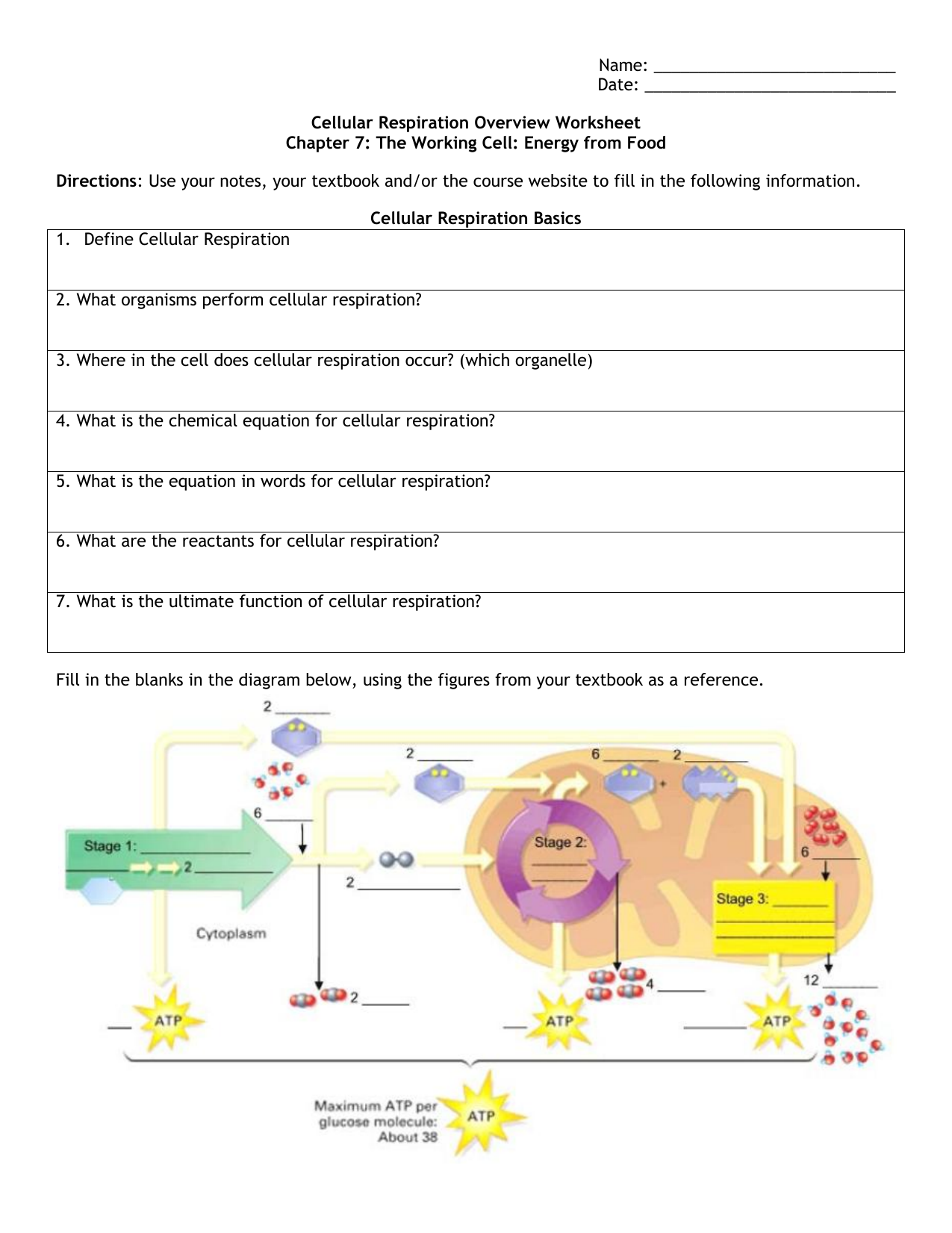
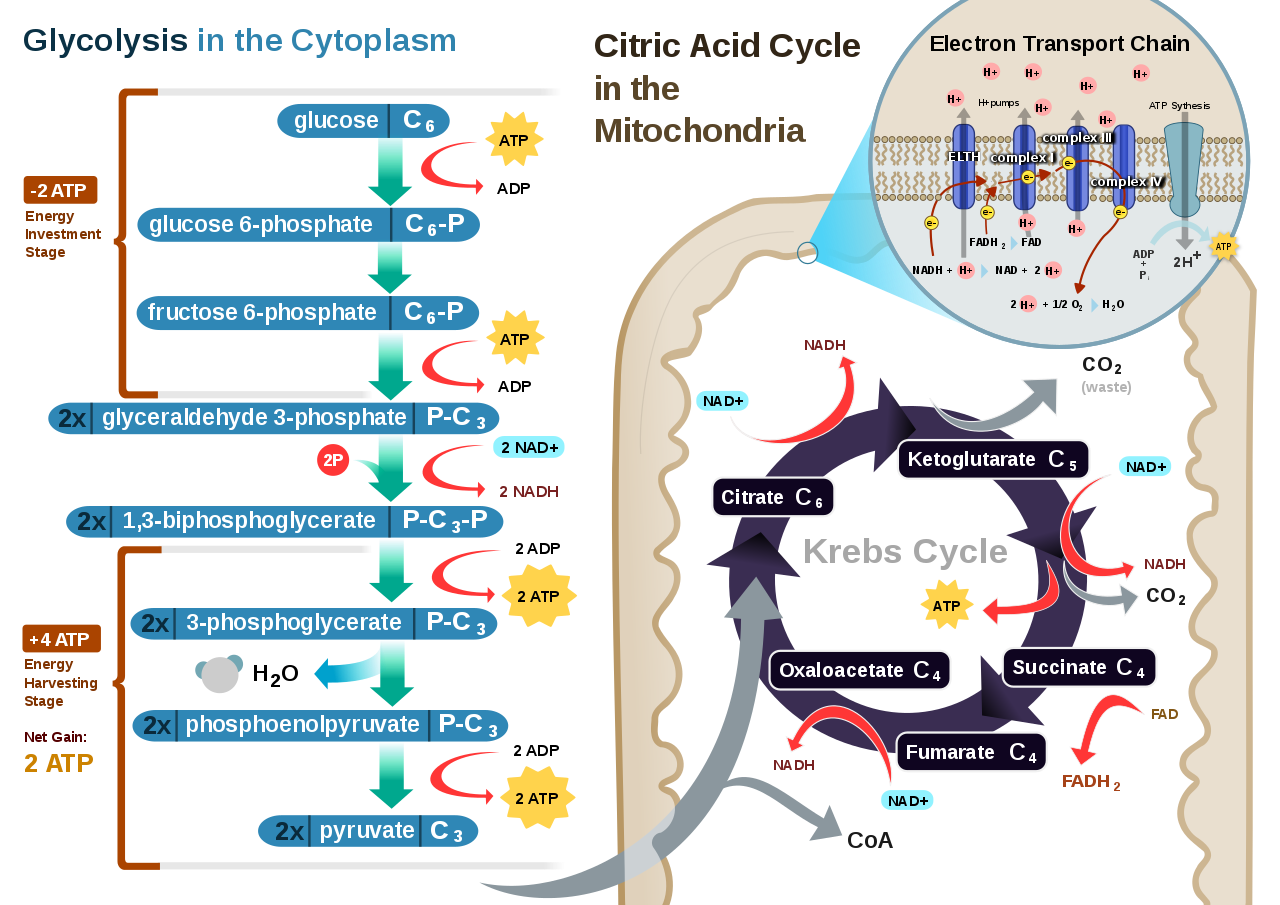
Understanding Cellular Respiration Here are three visual depictions of cellular respiration an equation an output description and an illustration. C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O 38ATP Glucose 6. The following are general representations formulae for both photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
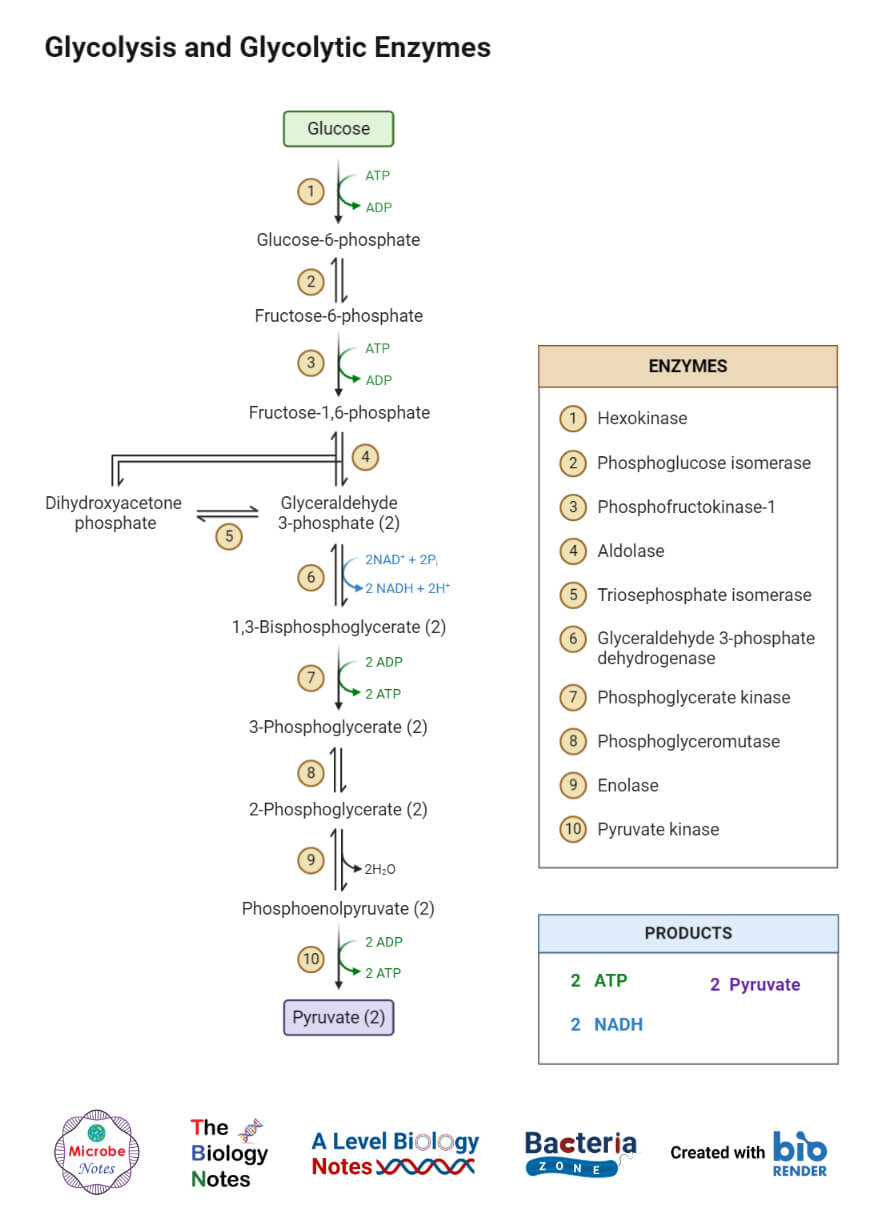
Also known as the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway it is the first step of cellular respiration. The cells break down the glucose molecule to convert its stored biochemical energy into energy-coin Adenosine triphosphate ATP. The simplified formula for aerobic cellular respiration is.
It is an exergonic reaction where high-energy glucose molecules are broken down into carbon dioxide and water. It is also known as a catabolic reaction as a large molecule like a carbohydrate is broken down into smaller molecules. Cellular respiration is defined as the conversion of fuel into energy and nutrients within the mitochondria and cytosol of cells.
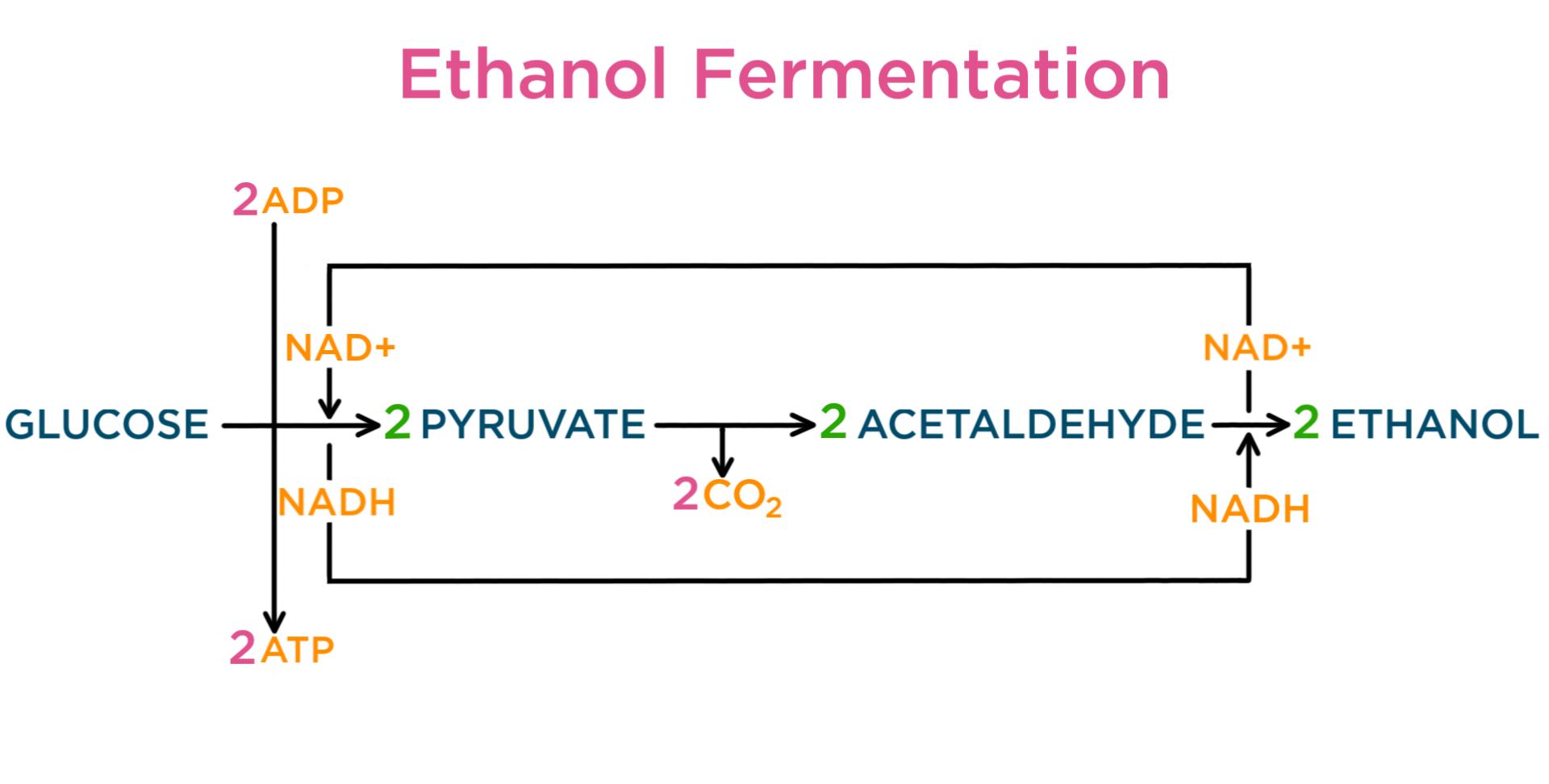
Aerobic or respiration in the presence of oxygen and anaerobic or respiration without oxygen. Respiration is the process in which organisms exchange gases between their body cells and the environment. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic processes.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration_3-58b9a5415f9b58af5c839e04.jpg)