Cell Membrane Structure And Function A Level

Animal Cell Structure Nucleus.
Cell membrane structure and function a level. The plasma membrane is impermeable to ions and most water-soluble molecules. -A double membrane sac which pinches off the end of organelles such as the RER or Golgi Apparatus and fuses with other membranes such as the RER Golgi or Plasma Membrane Function of Vesicles -Transport proteins and other substances between organelles and the outside of the cell. Images obtained through electron micrography reveal the bilayer structure of cell membranes.
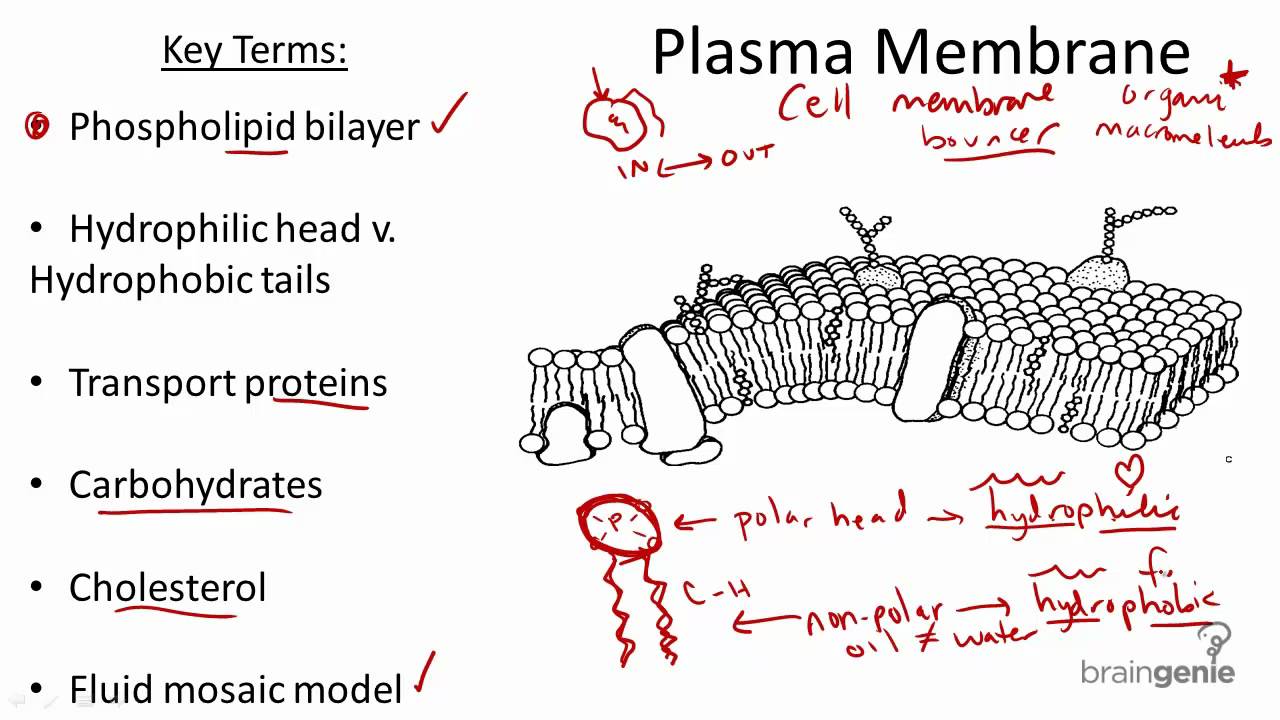
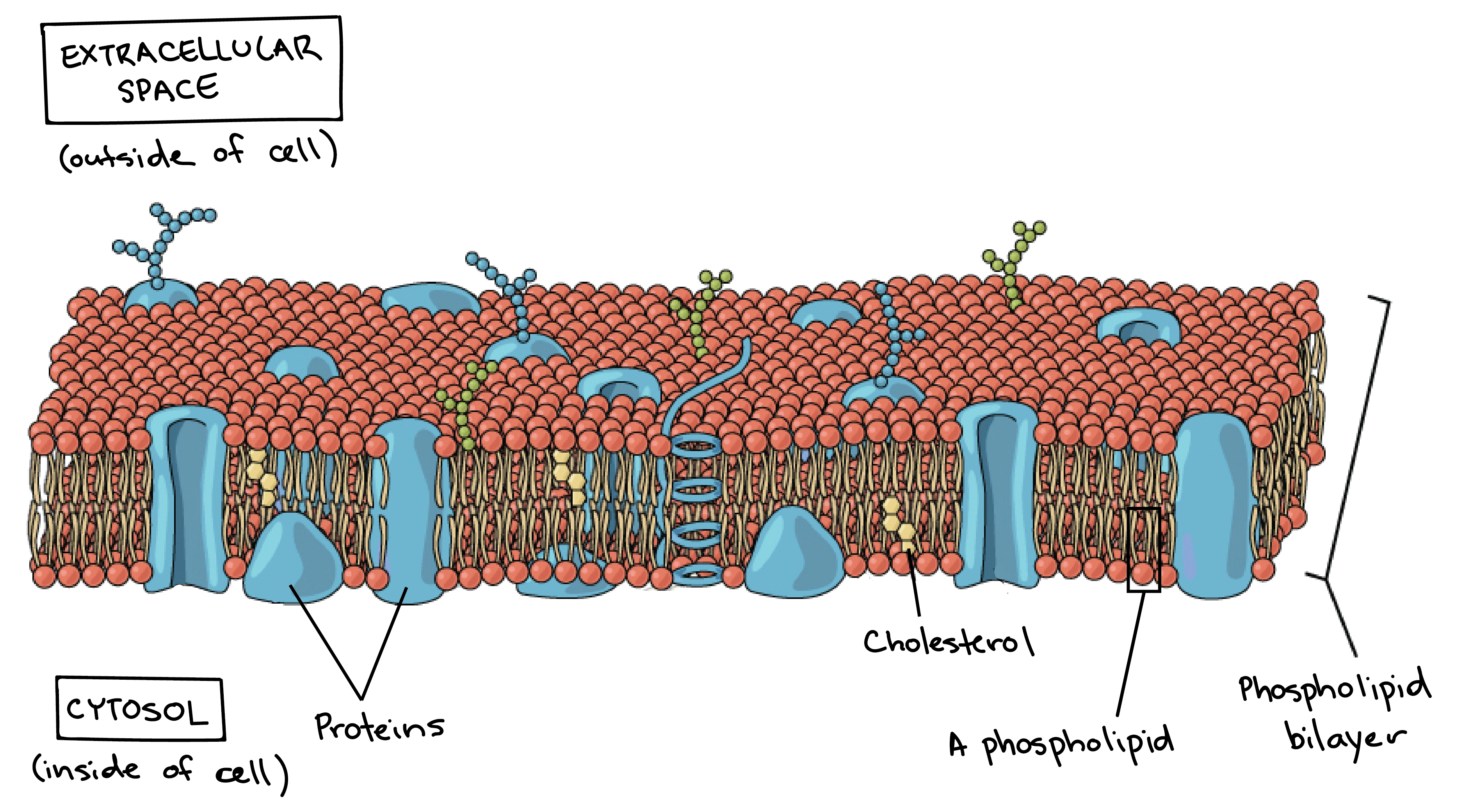
The cell wall and the cell membrane are the main components that function to provide support and structure to the organism. Form the basic structure of the membrane phospholipid bilayer The tails form a hydrophobic core comprising the innermost part of both the outer and inner layer of the membrane. Membranes are selectively permeable so are effective barriers in controlling what goes in and out of cells.
The liquid where all. 1 Isolate cells contents from outside environment 2 Regulate exchange of substances between inside and outside of cell 3 Communicate with other cells Note. Act as a barrier to most water-soluble substances the non-polar fatty acid tails prevent polar molecules or ions from passing across the membrane.
It separates the contents of the cell from the outside environment and controls the entry and exit of materials. This organelle is also referred to as plasma membrane. For eg the skin is made up of a large number of cells.
Formed from a phospholipid bilayer with the hydrophobic tails pointing towards each. Many membranes within the cell help to make different compartments for different chemical reactions to take place. Membrane Structure and Function All cells have a plasma or cell membrane which contains the cell.
The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment which protects the cell from its environment. Scanning electron micrograph SEM of adipocytes Ad Membrane Structure and Function Prokaryotic Cells. Holds the cell content controls the insouts structural forms cell recognition adhesion signaling transport of substances endoexocytosis Cytoplasm.